
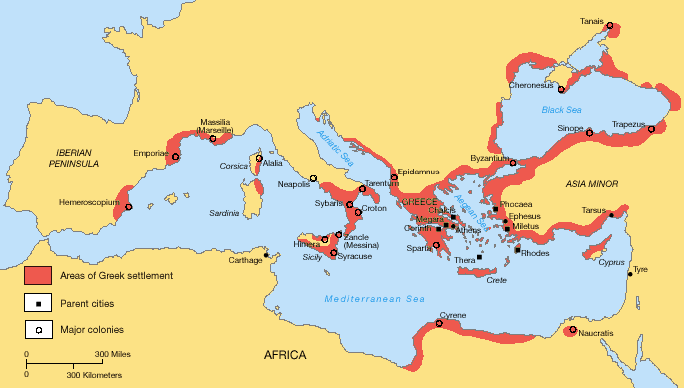
Or using the grid to your right you can click a photo to enter the main menus. If you'd just like to start your exploration of Italy with some ideas of places to go then I'd recommend starting at the highlighted must see Italy page. You can keep in touch with the latest developments in Italy, particularly important at the moment at the time of the pandemic, via my Italy Review Blog for which you'll find links below to the Facebook and Twitter pages. I've visited every place that's listed on the website which means I'm able to give useful advice for first-time visitors. The photos and descriptions on the website are all my own work and are the fruit of my extensive travels around the country. Alongside the major tourist destinations that you've already heard of, there are thousands of others that may come as a surprise with the intention of the website to provide inspiration for your future trips to the country. Throughout the three thousand pages of the website you'll find comprehensive tourist information, opinion and original photos. The Romans referred to this phenomenon as Magna Graecia, what we refer to as Great Greece because of the dense Greek populations they discovered throughout southern Italy. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.Italy Review is an independent guide to Italy, showcasing the very best that the country has to offer. The western Greeks: classical civilization in the western Mediterranean. The Greek world: art and civilization in Magna Graecia and Sicily. Sicily before history: an archaeological survey from the Paleolithic to the Iron Age. Sicilia e la Magna Grecia: Archeologia della Colonizzazione Greca d’Occidente (Manuali Laterza 314). Magna Graecia Published ApMagna Graecia is the term applied to those parts of southern Italy and Sicily that were colonised by the Greeks, beginning as early as the 8 th century BC. Archeologia della Magna Grecia (Manuali Laterza 29), 6th edn. Forme di identità, modi di contatto e processi di trasformazione. Warminster: Aris and Phillips.Īlbanese-Procelli, R.M. Sicily under the Roman empire: a Roman province, 36 BC – AD 365. Harvard Studies in Classical Philology 97: 35-50. Collection de l’Ecole française de Rome 251: 141-183. Actes de la recontre scientifique, Rome-Naples, 15-18 Novembre 1995. Italy is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, in Southern Europe. Most notably the Roman poet Ovid referred to the south of Italy as Magna Graecia in his poem Fasti. Italy (Italian: Italia ()), officially the Italian Republic or the Republic of Italy (Italian: Repubblica Italiana repubblika italjana), is a country that consists of a peninsula delimited by the Alps and several islands surrounding it its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Questions de métrologie, in La colonisation grecque en Méditerranée occidentale. Magna Graecia, meaning Greater Greece, was the name given by the Romans to Southern Italy as this area was extensively populated by Greek colonies in antiquity. American Journal of Archaeology 107: 145-180. The sanctuary of the divine Palikoi (Rochicella di Mineo, Sicily): fieldwork from 1995 to 2001. Scott (ed.) The nature and function of water, baths, bathing and hygiene from antiquity through the renaissance (Technology and Change in History 11): 43-59. Archimedes, the north baths at Morgantina and early developments in vaulted construction, in C. Tonfiguren im Grab: Fundkontexte hellenistischer Terrakotten aus der Nekropole von Tarent. The western Greeks: the history of Sicily and South Italy from the foundation of the Greek colonies to 480 B.C.
Taranto: Convegno di Studi Sulla Magna Grecia.ĭunbabin, T.J. Atti del 36 o Convegno di Studi sulla Magna Grecia: 475 -501. Consumption, cultural frontiers, and identity: Anthropological approaches to Greek colonial encounters, in Confini e Frontiera nella Grecità d’Occidente. Chicago (IL): University of Chicago Press.ĭietler, M. Cults, territory, and the origins of the Greek city-state. Greeks, Romans and Barbarians: spheres of interaction. Parra (ed.) Magna Graecia: Archeologia di un Sapere: 33-40. This area may also be thought of as forming part of 'western Hellas'.

The Romans called the Greek colonies in southern Italy, excluding Sicily, Magna Graecia (meaning extended or 'greater Greece'). Megale Hellas, Magna Graecia, Italía: Dinamiche di Nomi, in S. Magna Graecia The Greeks called south-western Italy Oenotria. Washington (DC): Center for Hellenic Studies.Ĭordano, F. Malkin (ed.) Ancient perceptions of Greek ethnicity: 113-157. Kupara, a Sikel nymph? Zeitschrift für Papyrologie und Epigraphik 126: 177-185.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
